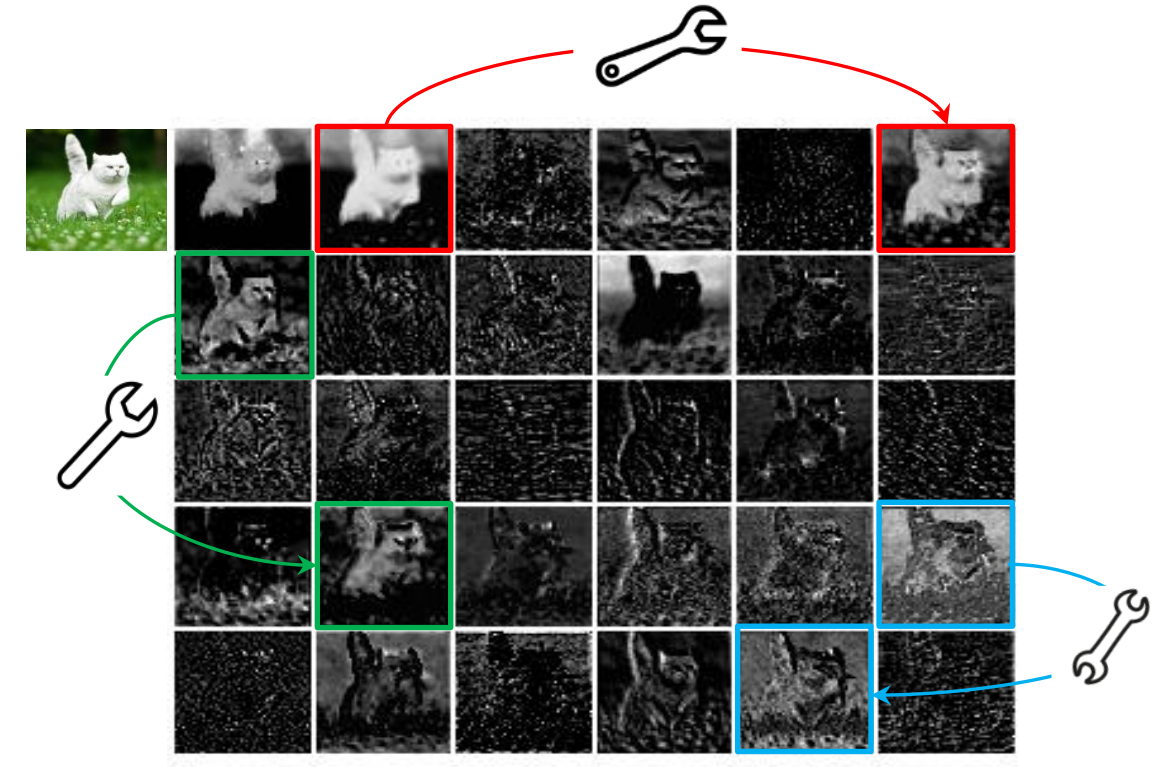
这是一篇讲低光照人脸检测的论文。原论文(HLA-Face Joint High-Low Adaptation for Low Light Face Detection)。
- 充分利用现有的正常光数据,并探索如何将面部探测器从正常光线调整到低光。这项任务的挑战是,正常和低光之间的差距对于像素级和物体级别来说太大而复杂。因此,大多数现有的lowlighenhance和适应方法不达到所需的performance。
- 本文是DARK FACE为基准,针对现有的正常照度图像,将图像调整成低照度图像,不需要标签
- 一个是像素级外观的差距,例如不足,照明,相机噪声和颜色偏置。另一个是正常和低光场景之间的物体级语义差异,包括但不限于路灯的存在,车辆前灯和广告板。传统的低光增强方法[5,6]设计用于提高视觉质量,因此不能填充语义差距,
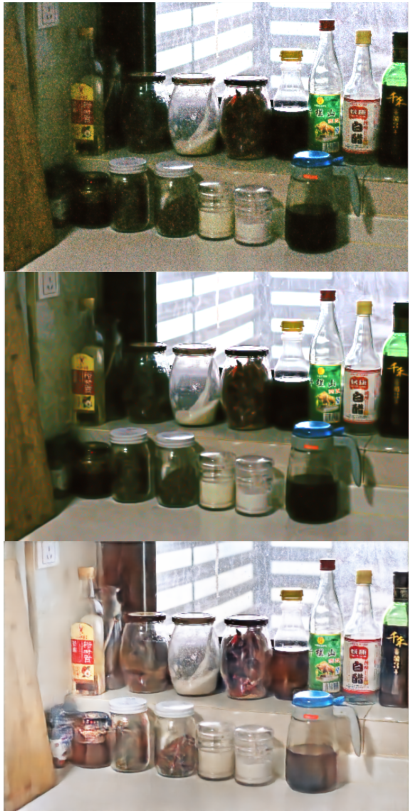
- 通过使低光图像亮起并扭曲正常光图像,我们构建位于正常和低光之间的中间状态。
摘要:
Face detection in low light scenarios is challenging but vital to many practical applications, e.g., surveillance video, autonomous driving at night. Most existing face detectors heavily rely on extensive annotations, while col- lecting data is time-consuming and laborious. To reduce the burden of building new datasets for low light condi- tions, we make full use of existing normal light data and explore how to adapt face detectors from normal light to low light. The challenge of this task is that the gap between normal and low light is too huge and complex for both pixel-level and object-level. Therefore, most existing low- light enhancement and adaptation methods do not achieve desirable performance. To address the issue, we propose a joint High-Low Adaptation (HLA) framework. Through a bidirectional low-level adaptation and multi-task high- level adaptation scheme, our HLA-Face outperforms state- of-the-art methods even without using dark face labels for training. Our project is publicly available at: [https: //daooshee.github.io/HLA-Face-Website/](https: //daooshee.github.io/HLA-Face-Website/)