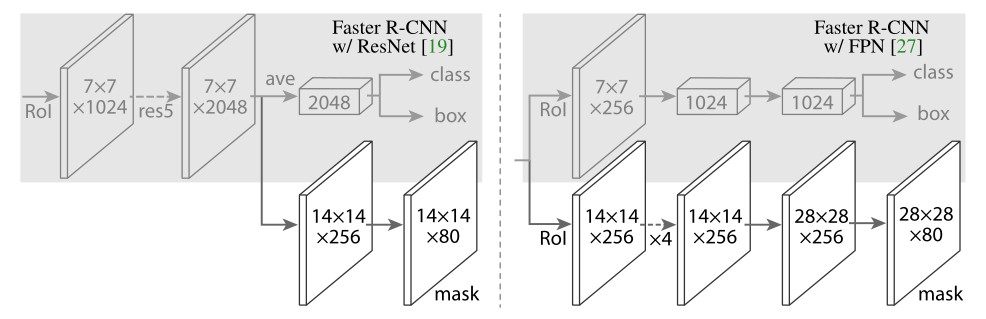
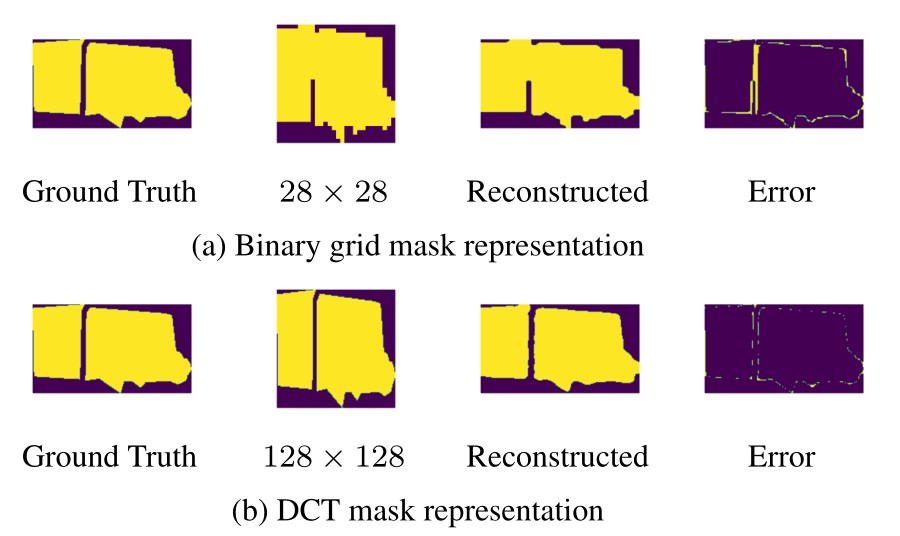
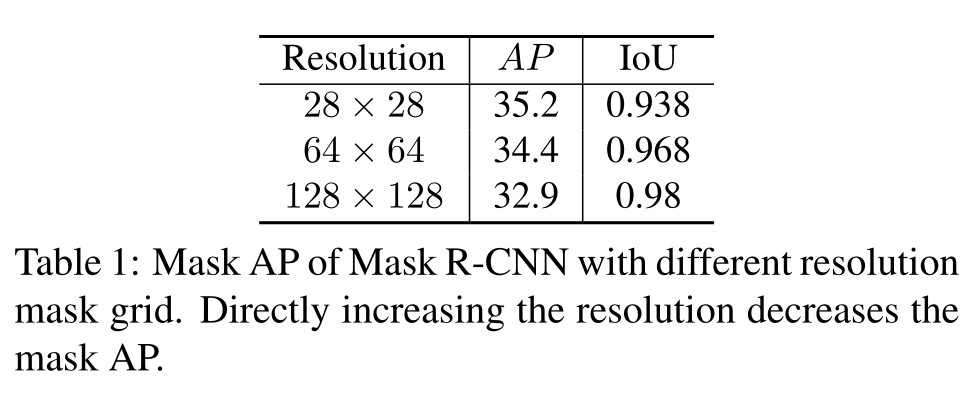
Kai Xu, Minghai Qin, Fei Sun, Yuhao Wang, Yen-Kuang Chen, Fengbo Ren
Deep neural networks have achieved remarkable success in computer vision tasks. Existing neural networks mainly operate in the spatial domain with fixed input sizes. For practical applications, images are usually large and have to be downsampled to the predetermined input size of neural networks. Even though the downsampling operations reduce computation and the required communication bandwidth, it removes both redundant and salient information obliviously, which results in accuracy degradation. Inspired by digital signal processing theories, we analyze the spectral bias from the frequency perspective and propose a learning-based frequency selection method to identify the trivial frequency components which can be removed without accuracy loss. The proposed method of learning in the frequency domain leverages identical structures of the well-known neural networks, such as ResNet-50, MobileNetV2, and Mask R-CNN, while accepting the frequency-domain information as the input. Experiment results show that learning in the frequency domain with static channel selection can achieve higher accuracy than the conventional spatial downsampling approach and meanwhile further reduce the input data size. Specifically for ImageNet classification with the same inpu t size, the proposed method achieves 1.41% and 0.66% top-1 accuracy improvements on ResNet-50 and MobileNetV2, respectively. Even with half input size, the proposed method still improves the top-1 accuracy on ResNet-50 by 1%. In addition, we observe a 0.8% average precision improvement on Mask R-CNN for instance segmentation on the COCO dataset.
Comments: Accepted to CVPR 2020