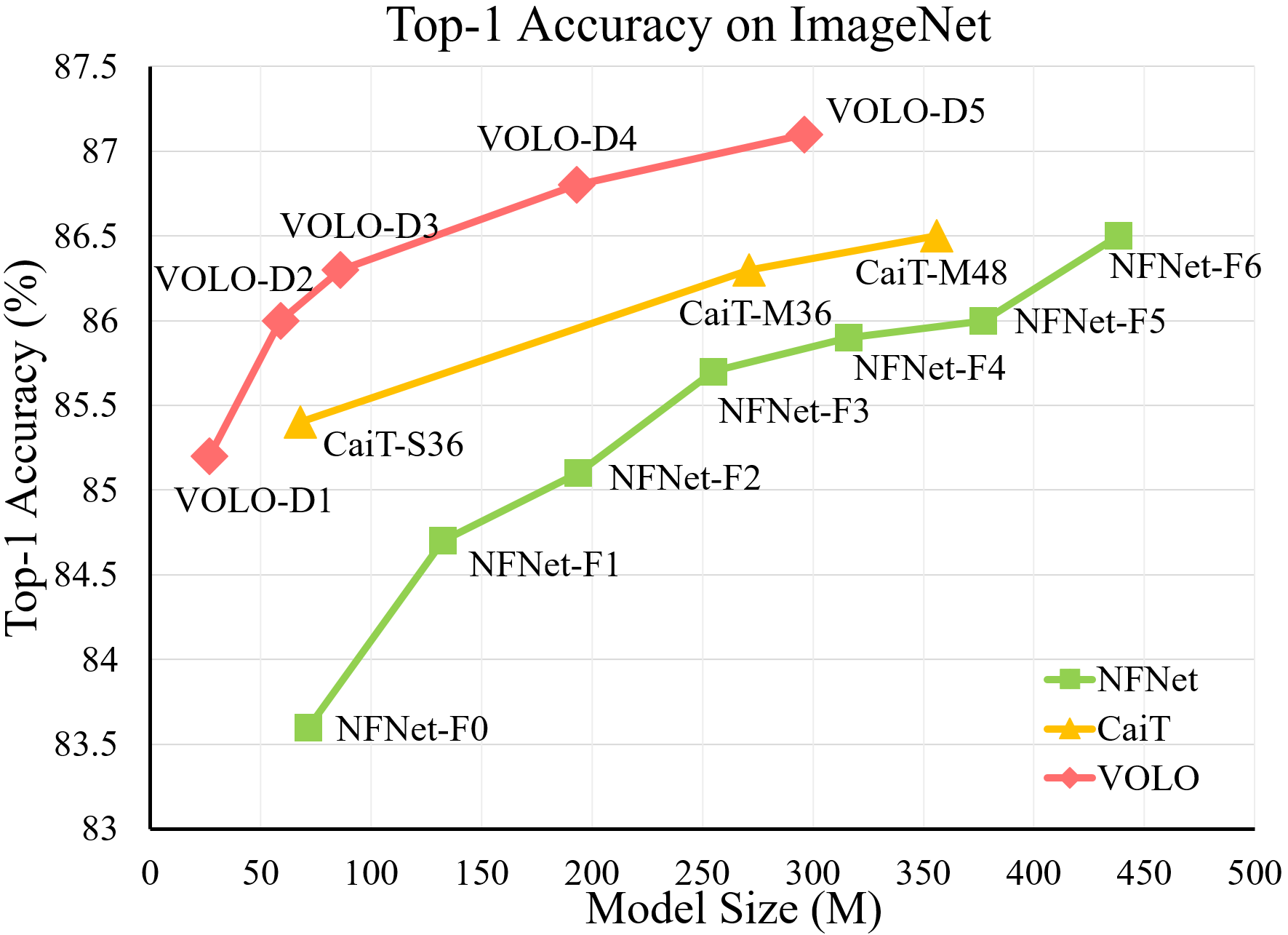
论文名称: MSR-net:Low-light Image Enhancement Using Deep Convolutional Network
论文作者: Liang Shen, Zihan Y ue, Fan Feng, Quan Chen, Shihao Liu, Jie Ma
Code: None
这是一篇讲解基于Retinex理论使用卷积神经网络进行低照度增强的论文。
- 基于MSR传统理论构造卷积神经网络模型
- 直接学习暗图像和亮图像之间的端到端映射
Abstract (摘要)
Images captured in low-light conditions usually suffer from very low contrast, which increases the difficulty of sub-sequent computer vision tasks in a great extent. In this paper, a low-light image enhancement model based on convolutional neural network and Retinex theory is proposed. Firstly, we show that multi-scale Retinex is equivalent to a feedforward convolutional neural network with different Gaussian convolution kernels. Motivated by this fact, we consider a Convolutional Neural Network(MSR-net) that directly learns an end-to-end mapping between dark and bright images. Different fundamentally from existing approaches, low-light image enhancement in this paper is regarded as a machine learning problem. In this model, most of the parameters are optimized by back-propagation, while the parameters of traditional models depend on the artificial setting. Experiments on a number of challenging images reveal the advantages of our method in comparison with other state-of-the-art methods from the qualitative and quantitative perspective.
本文提出了一种基于卷积神经网络和视网膜理论(Retinex Theory)的低照度图像增强模型。证明了多尺度视网膜等价于一个具有不同高斯卷积核的前馈卷积神经网络。考虑一种卷积神经网络(MSR网络),它直接学习暗图像和亮图像之间的端到端映射。